Cash flow statement analysis
The statement of cash flows is one of the required statements that must be published in the financial statement of a company. The statement of cash flows or cash flow statement is so important, that it must be presented every year so far the income statement is also presented in the period concerned. This means that if a company chooses to ignore the preparation of the balance sheet (statement of financial position) but presents the income statement, then the statement of cash flow must be prepared.
Now let us discuss some of the uses of a cash flow statement
- Statement of cash flows provide the user information that can be used to analyze liquidity, solvency and financial flexibility of a company.
- It shows the ability of a company to generate positive future cash flows and meet obligations as they come due.
- It shows the effect of financing and investing activities on the company’s financial position.
- It provides information on the company’s need for external financing
- It helps to assess the reasons for differences between net income and net cash receipts and payment.
Classification of the statement of cash flows
The statement of cash flows can be broken down into three main activities which are:
- Operating activities
- Investing activities
- Financing activities
Let’s take a look at each one of them:
Operating activities: Operating activities are “business as usual” activities. They are part of the company’s core business activities and central operations. Operating activities generally generate revenue and expenses for the company. These activities directly affect an organization’s inflow and outflow, and determine its net income. Examples of items classified as operating activities include:
- Cash received from customers and paid to suppliers;
- Interest and dividends received from debt and equity investments respectively;
- Taxes and refund of taxes;
- Interest paid on bonds and other debt (loan, leases, mortgages).
Investing activities: Investing activities are activities undertaken by the company to secure or generate future economic benefits, profit or returns. Investing activities may include:
- Acquiring and disposing off debt instruments;
- Making and collecting loans to other parties;
- Purchasing and selling of fixed assets;
- Acquiring and disposing of available-for-sale or held-to-maturity securities.
Financing activities: Financing activities are transactions that affect long term liabilities and equity. Funds received from financing activities may be used to fund operations or expansions. Financing activities under the statement of cash flows are the activities a company undertakes to raise capital to finance the business.
Financing activities include:
- Issuing of stock;
- Issuing of debt securities;
- Obtaining and repaying a loan;
- Treasury stock transactions;
- Repayments of debt obligation.
The statement of a cash flow in its preparation has a natural check mechanism. The check is that the total increase or decrease in cash can be easily derived from a comparison of the previous and current year’s current asset items (cash and cash equivalents) in the statement of financial position.
There are two methods of preparing the statement of cash flow. They are
- The indirect method
- The direct method
The two methods ultimately lead to the same result. The difference is that in the direct method, each individual line in the income statement is adjusted, while in the indirect method, the net income figure is adjusted. The main aim of the two methods is to take out the effect of non cash and non operating activity transactions such as depreciation expenses and sale of fixed assets respectively.
Example of direct method of reporting cash flow from operating activities:
| $ | |
| Cash receipts from customers | XXX |
| Cash paid to suppliers | (XXX) |
| Cash paid to employees | (XXX) |
| Interest paid | (XXX) |
| Dividend received | XXX |
| Income taxes paid | (XXX) |
| Net cash from operating activities | XXXX |
Example of indirect method of reporting cash flow from operating activities
| Net income | XXXXX |
| Adjustments for: | |
| Depreciation | XXX |
| Provision for losses on accounts | XXX |
| Gain on sales of assets | (XXX) |
| Increase in trade receivables | (XXX) |
| Decrease in trade payables | (XXX) |
| Cash generated from operations | XXXX |
It is the preparation of the cash flow from operating activities that differs between the indirect method and the direct method. Preparation of the cash flow from investing activities and financing activities is basically the same using either the direct method or the indirect method.
Investing activities affect a corporations long term assets. Investments in long term assets to the company include gains or losses resulting from investments in the financial markets (stocks, bonds), operating subsidiaries and changes resulting from the buying and selling of capital assets such as plant and equipment. A negative cash flow from investing activities may mean that the company is purchasing long term assets for expansion activities or because of an encouraging future prospect or outlook for the company; with the above, a negative cash flow from investment activities is not necessarily a bad thing.
A positive cash flow from investing activities is not always good. It may mean that the company is not generating enough cash to service short term debts and needs to sell off investments to generate short term cash, and investments may even be sold at a price lower than the market value of the investment.
Example of cash flow from investing activities
| Add cash received from sale of investment | XXXXX |
| Add Cash received from sale of land | XXXXX |
| Add proceeds from sale of equipment | XXXXX |
| Less payment for purchase of investments | (XXXXX) |
| Less payment for purchase of plants & equipment | (XXXXX) |
| Less payment fro the purchase of land | (XXXXX) |
| Less cash payments for the purchase of buildings | (XXXXX) |
| Net cash from investing activities | XXXXXX |
Cash flow from financing activities
These are payments made or received by a company when creating its capital structure. It includes issuing and buying back stock as well as issuing debt securities such as bonds and notes.
| Cash received from issuance of stock | XXXXX |
| Cash received from the issuance of long term debt | XXXXX |
| Cash paid for retirement of bonds payable | (XXXXX) |
| Principal payments under capital lease obligations | (XXXXX) |
| Cash paid for dividends | (XXXXX) |
| Net cash provided by financing activities | XXXXXX |
Disclosures: When the statement of cash flow is prepared using the direct method, a disclosure of the reconciliation between net income and cash flows from operating activities is required. When the statement of cash flow is prepared using the indirect method, a disclosure of the amount of cash paid for interest and cash paid for taxes is required.
Example:
Now that we have looked at the major activities in a cashflow statement, let’s go ahead to see themcombined to form a full cash flow statement.
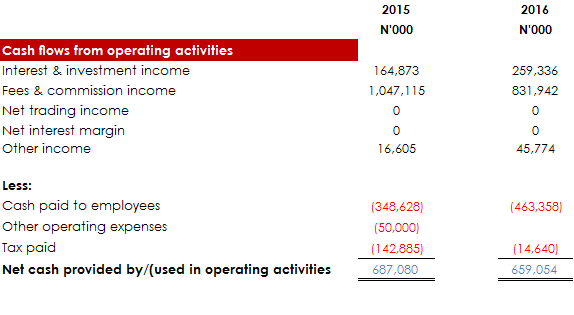
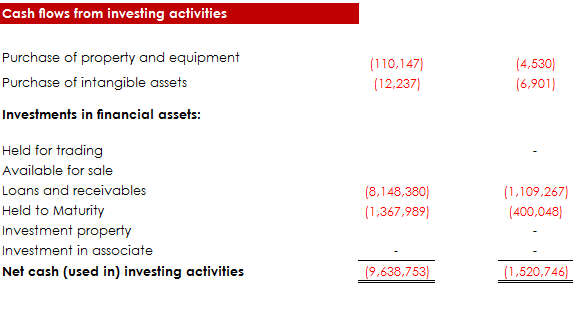
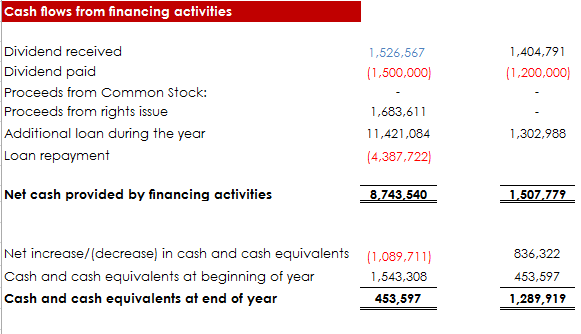
Recommended Reading
Baruch Englard., Schaum’s Outline of Intermediate Accounting II






Leave a Reply