Introduction to Sales Planning
In sales planning, the sales manager, working in concert with the marketing manager and top management is expected to come up with a sales forecast figure for a given business period. Because salesmen have direct responsibility of realizing the sales forecast of firms, then they should be involved in doing the forecast.
The sales forecast figure represents the expected sales figure for the firm and it forms the basis foer all organizational planning i.e. organizational budgeting, production schedule and purchasing schedule depend largely on sales forecasting.
Once the level of sales expected to be achieved by the sales force is known, it then falls on the lap of the sales manager to plan how to achieve the target. It then becomes necessary for the sales manager to estimate the amount of selling efforts needed to achieve the desired sales target. With this known, the sales manager will be able to know the number of saes men needed for the realisation of the target.
Based on the expected sales target, the sales manager would allocate quota to his salesmen. The aggregate of the quotas should equal at least the expected sales target.
Sales Management Objective
The traditional method of stating objective is in terms of sales volume. This has been criticized. The criticism against this approach stems from the fact that if salesmen concentrate primarily on sales volume, they may neglect the cost of achieving such targets to the detriment of the organization’s profitability. The better way of stating sales force objective is in terms of contribution to profit. If a salesman is given a profit level as a sales target, he would be better minded to consider selling cost with a view to minimizing it while maximizing sales volume at the same time. Whether stated in terms of profit or sales volume, sales target for salesmen can be expressed on the basis of product, territory, customers.
What is a market?
It is any arrangement where buyers and sellers are in close contact for the purpose of exchange (From Economics point of view). Market is the set of potential and actual buyers of a product (marketing point of view by phillip cortler). Let us now look at participants in a market. Participants in a market include customers, clients grouped under buyers and sellers and advocate grouped under sellers. A customer is someone who buys from very many sources; a client is one who buys from only one source. A seller provides the goods for sale, while an advocate is a praise singer who tries to convince people to purchase the products. He sings praises to the high heavens and highlights the best features of a product.
Market Potential:
It is the maximum possible sales opportunity open to all sellers of a product within a specified period of time, i.e it tries to measure the maximum sales opportunities of all firms within an industry.
Sales Potential :
It is the maximum possible sales opportunity open to a specific firm or company that is selling a product within a specified period of time. I.e it helps to measure or explore the maximum sales opportunity of a firm.
Market Forecast:
This is an estimate of the expected sales of all firms in a specified period under the firm’s respective marketing plan. That is, it measures what all firms producing a product will sell within a period.
Sales Forecast:
This is an estimate of the expected sales of a particular company within a specified period.
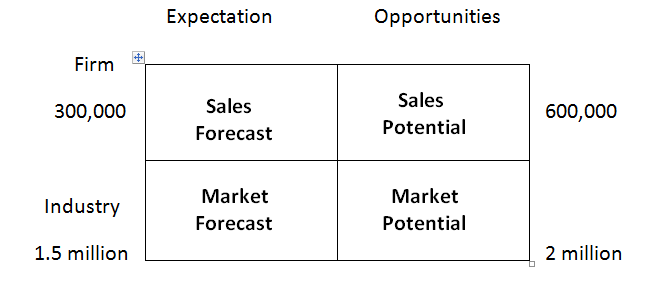
Example: Mercury Produce automotive batteries. Based on research, they are able to establish that Nigerians would buy up to 2,000,000 units of battery every year. This is the market potential. But they can only produce 1,500,000 units a year; that is their expectation or market forecast or estimate.
Forecasting:
Forecasting is anticipating what buyers are likely to do under a specific set of marketing condition. While forecast serves as goals to be accomplished , forecasting is the process of establishing these goals.
The techniques of sales forecasting or method of selling forecast figures include:
- The quantitative – Statistical
- The qualitative – non-statistical
Qualitative:
This involves the use of simple average with standard deviation, regression analysis or trend analysis
Non- Statistical or Qualitative
This involves the use of survey of buyers intention, composite of sales force opinion, and expert method or jury of executive opinion.
Recommended Readings
Schewe, Charles D., and Alexander Hiam, The Portable MBA in Marketing
Gary Armstrong., and Philip Kotler, Marketing an Introduction
Philip Kotler., and Kevin Lane keller, Marketing Management (14th Edition)






Leave a Reply