6th July 2015
Thursday!. Mpr is looming and everybody is extremely busy including me. I was given a report to allocate AUM (Asset under Management), admin fees, and also to do the individual P & L of marketers and more. Did i say a report?, i meant multiple reports. I was so tired after this. I heard disturbing news later that the wife of one of our staff died on this day, what terrible news. I was devastated on hearing this. life is so unfair, but what can we do? The Lord gives and takes away. It can be very painful, but he knows best.
So I went to the spot near my university and read something on private equity. The summary of what I read is as follows:
Introduction to Private equity
PRIVATE EQUITY
Private equity is not regulated unlike the capital market which is regulated by the securities and exchange commission here in Nigeria. To delve into this type of funding requires huge money and financial capability and so the people that mostly partake in it are sophisticated investors such as pension plans, financial institutions, endowments and high net worth individuals.
There are three categories in the life of a private equity which are:
- Venture capitals: They are equity investments in immature high growth companies with high burn rate. They are two stages of the venture capital, they are:
- Early stage: At this stage, the costs which would be incurred would be at the highest. There might not necessarily be returns during this stage. Costs such as research cost, start-up costs would be incurred.
- Expansion stage: This is the second stage in this category, they are investments in companies that are already established and need more capital to expand their operational activities.
- Buy- out: They are debts and equity used to purchase the shares of a mature public company. Types of buyout include:
- Management buyout: existing managers of a firm take it private
- Management buy-in: Managers outside a firm take the company private
- Public to private: Public firms are purchased and the target firm is taken private
- Leveraged buy out: Here the debt is used to purchase the shares of a public company
- Mezzanine: Subordinated debt investments (with equity warrants or conversion options) in established companies seeking expansion or transition financing. eg
- Rescue (turnaround capital): Financing for companies that are distressed and at the brink of liquidation.
- Replacement capital: Financing for purchasing a firm’s share capital from another private equity firm.
The main difference between buyout funds and venture capital finds is that buyout funds are for established businesses, either for restructuring the ownership of the company or taking a public company private. Venture capital on the other hand invests in early stage or expansion stage companies that seek to gain market share in a new and high growth market.
In private equity funds, there are two types of partners which are limited partners and general partners. Limited partners contribute funds to form a pool of funds for investment purposes, and the general partner through his expertise managers the funds, invests them and takes out management fees and or carried interests.
Some advantages of allowing a general partner manage is that there is more expertise in managing funds because the general partners are skillfully trained and have a lot of experience In managing such funds. Also there is limited liability, low taxes and high transparency.
Funds of funds are funds from a pool of capital aggregated from multiple investors. Funds of funds primarily engage in three types of transactions, which are limited partnership investments, direct investments in private equity and secondary market purchase of private equity.
A company might also choose to run private equity through in- house management. This is when the company chooses to source investment opportunities and use its in house management expertise to run it. It might be expensive to run and there might not be proper incentives for the in house managers, which might make them leave for other funds.
Benefits of funds of funds over in-house management approach include:
- Outsourcing expertise in fund selection
- Diversification
- Immediate access to private equity partnership
- Proper incentive structure
The disadvantage of a fund of fund structure is that the general managers collect management fees as a fixed percentage of the asset under management. Also they collect carried interests, on the revenue made, which is like 20%.
The private equity also loses control of the fund.
There are 3 phases in the life cycle of the general partner and limited partner situation. They are
- The entry and establish phase
- The build and harvest phase
- The decline or exit phase
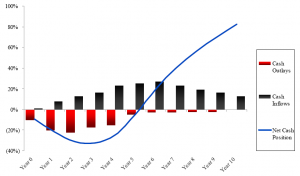
J CURVE
There is a j curve concept in private equity which believes that at the beginning of setting up a fund, there is a decline in the value of the fund due to the costs such as the set up costs, management fees and valuation policy. Successful investments are realized in later years, which makes it rise at some point, thereby forming the j curve.
Because of the common j curve progression of returns, it would be unfair comparison to weigh the returns of funds that are at different points in the life cycle.
DIAGRAM OF JCURVE
Recommended Reading
Alternative Investments: CAIA Level I (Wiley Finance)






Leave a Reply