Porter’s Business Strategies
Michael porter with regard to business level strategy proposes two generic competitive strategies for outperforming other companies in the competitive space in a particular industry. The strategies are generic in the sense that it can be utilized by any firm within an industry notwithstanding its size. The two strategies are lower cost and differentiation strategies.
Lower Cost Strategies
This is when a firm has competitive advantage through the lower cost of products and services relative to its competitors. We can sum it up as the ability of a company to design, produce, market and distribute a comparable product more efficiently than its competitors. Lower cost strategies can be further broken down into cost leadership and cost focus.
1)Cost Leadership: Cost leadership occurs whereby a company targets a broad mass- market and tries to gain competitive advantage by producing products at a minimal cost and more efficiently than its competitors. Cost leadership inculcates aggressive construction of efficient scale facilities, tight cost and overhead control, avoidance or reduction of marginal customer accounts and vigorous reduction of costs in the areas of research and development, advertising, sales force etc. Due to the conscious efforts in reduction of costs, a cost leader is often able to offer products at a lower price compared to its competitors and still able to rake in satisfactory profit. This is the core of the strategy as the firm seeks to win market share by appealing to cost-conscious or price-sensitive customers.
How to achieve cost leadership
There are three ways of achieving cost leadership strategies, and they are:
- Production of high volumes of output through economies of scale. Economies of scale are the cost advantages a company obtains through increased level of production , scale of operation, size and output which sees the cost per unit of output normally decreasing with increasing scale, as fixed costs are spread across product or service departments, thereby resulting in a lower unit cost.
- Reduction of direct and indirect operating costs: A company can attain the level of a cost leader by keeping both direct and indirect costs to a barest minimum. This is achieved by offering high volumes of standardized products, limiting customization and personalization of service and offering basic products without room for unnecessary extras that do not add value to the overall quality of the product.
- Control over supply to ensure low costs: If a company cannot practice backward integration, it should ensure that it builds a solid relationship with its suppliers to ensure costs are kept at a minimal level. Reduction of supply costs could be achieved by bulk buying to ensure quantity discounts, squeezing suppliers on price, working with vendors to keep inventories low.
2) Cost Focus: Cost focus on the other hand is a lower cost strategy that focuses on a narrow market, for example a particular geographic market or a particular buyer group. The company decides to serve a particular niche and dedicates its services to the niche while excluding other niches.
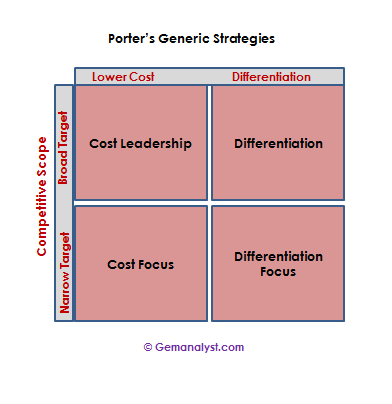
Differentiation Strategies
Differentiation strategies like the name implies is based on the company’s ability to differentiate its product from that of its competitors. The competitive advantage lies in the special features incorporated into the products or services being offered. The special features may include after sales services, free upgrades for the first year (for digital products) and so much more. Differentiation strategies can also be broken down into differentiation and differentiation focus.
1)Differentiation: Differentiation like cost leadership is aimed at the broad mass market, but unlike the cost leadership involves the marketing of products and services that are thought to be unique in its industry. Due to the perceived uniqueness, the company can afford to charge a premium for its products. To successfully pass on costs to consumers and charge a premium, the company seeks to increase its brand loyalty. When brand loyalty is increased, the sensitivity of the buyer to price reduces.
2) Differentiation Focus: Differentiation focus like cost focus also concentrates on a particular geographical market or buyer group, but also markets products and services that are perceived to be unique in its industry. In using differentiation focus, a company or business unit seeks differentiation in a target market.
Recommended Readings
Frank Rothaermel., Strategic Management: Concepts and Cases
Gregory Dess., Alan Eisner., GT Lumpkin., Geryy McNamara., Strategic Management: Creating Competitive Advantages
Recommended Courses
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign; Corporate Strategy
University of Virginia; Business Growth Strategy
University of Virginia; Business Strategy in Practice (Project-centered Course)






Leave a Reply